
Cross-border
economic
development
31
Territory portraits: economic development on different borders
France - Italy - Monaco
Comparison of framework
conditions
Framework conditions are fairly similar between France and Italy: GDP
per capita in terms of purchasing power, with the European average
(27 countries) giving the base of 100, stood at 98 for Italy in 2013 and
108 for France.
50
Businesses are taxed at one third of their profits in
France
51
and at 27.5% in Italy. After Germany and France, Italy is the
third-largest economy in the euro area. The two countries are one
another’s second trading partner.
The Principality of Monaco only taxes companies which generate more
than 25% of their profits outside the principality,
52
at a rate of 33.3%.
Apart from this, no tax is applied, neither on companies nor on natural
persons. Monaco has signed just one bilateral tax agreement, which is
50
Source: Eurostat.
51
Up to €38,120 profit, a reduced rate of 15% is applied.
52
As well as companies whose activity in Monaco consists in collecting revenue from patents or
royalties on literary or artistic property.
with France. This allows the taxation of French residents in Monaco as
though they were within French territory. In addition, the same level of
VAT is charged in France and Monaco. This agreement therefore serves
to limit the tax differences between France and Monaco.
Territories close to the border face particular constraints with respect to
land: from the coast up along the Roya Valley, on both the French and
Italian sides, available land is very scarce as, in addition to the limitations
of the physical geography, a large part of the territory is a protected
natural area.
53
With urbanisation having reached its limit (no more land
available), there are strong tensions between demand for housing for
working people, houses bought by retired people wanting to settle in
the area and tourism (rented accommodation and second homes).
53
Available land is particularly scarce in the coastal area (32% of artificially-constructed land as
compared to less than 4% in the middle and upper parts of the region), as well as in the whole
of the Menton-Roya Valley employment area, 93% of which consists of natural spaces that are
difficult to build on (geography and protection of the countryside).
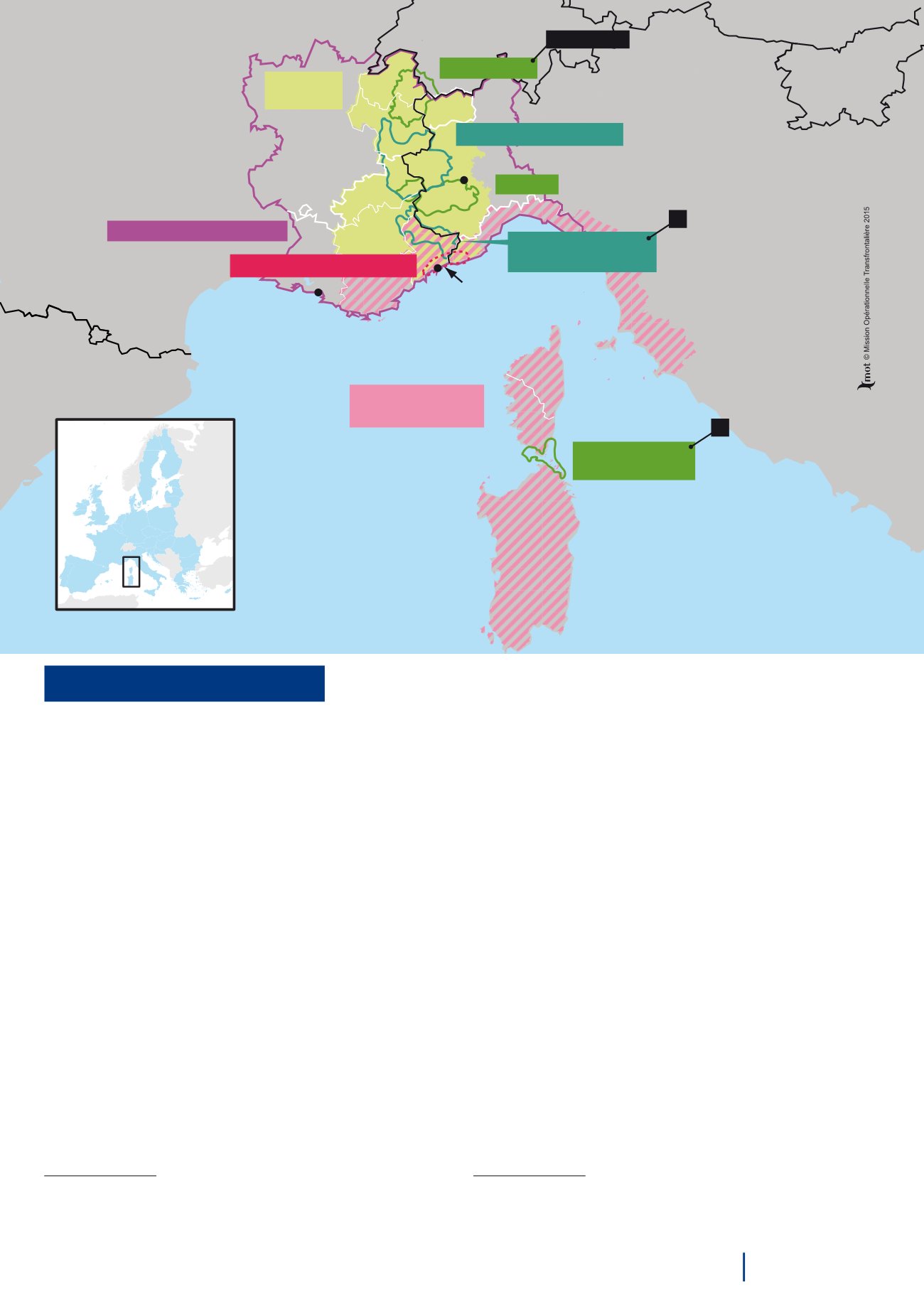
Portrait of a territory
Parc Marin International
des Bouches de Bonifacio
INTERREG
Italy-France Maritime
Franco-Italo-Monegasque Riviera
Haute-Savoie
Savoie
Hautes-
Alpes
Alpes-de-
Haute-Provence
Var
INTERREG
ALCOTRA
RHÔNE-ALPES
PACA
PACA : Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur
LIGURIA
AOSTA VALLEY
PIEDMONT
CORSICA
SARDINIA
TUSCANY
Alpes-
Maritimes
Alps–Mediterranean Euroregion
Conference of the High Valleys
FRANCE
SWI TZERLAND
MONACO
I TALY
Mont Viso
Mont Blanc Area
International Marine
Park of Bonifacio
EGTC
Marseille
Nice
Turin
European Park of
Alpi Marittime-Mercantour
EGTC ( under creation )
EGTC
Haute-Corse
Corse
du Sud



















